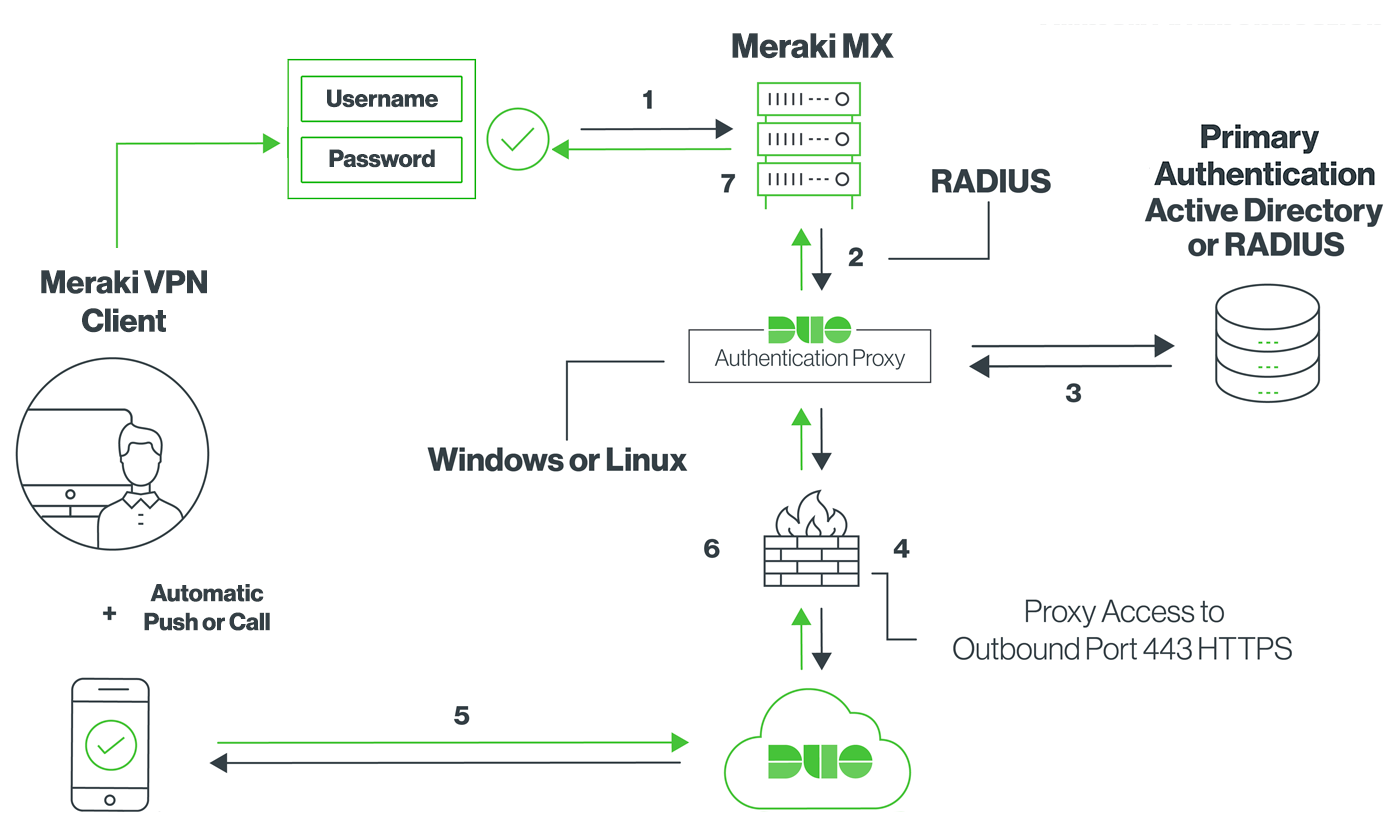
Auto VPN™ self-configuring site-to-site VPN; Client VPN (IPSec L2TP), limit 2 authorized users (with Meraki-hosted authentication only) VLAN and DHCP services; 802.1x wired port authentication; Static routing; User and device quarantine; Integrated Wireless 4 SSIDs; 2 × 802.11a/b/g/n/ac (2.4Ghz or 5 Ghz), 2x2 MU-MIMO with 2 spatial streams. Meraki Client VPN uses the Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) to transmit and authenticate credentials. PAP authentication is always transmitted inside an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX security appliance using strong encryption. When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard. Open Start Menu Control Panel, click on Network and Internet, click on View network status and tasks.

By default, the Client VPN timeout on the Meraki Security Appliances is 15 seconds. For there to be enough time for the authentication to complete this must be extended. To extend this you will have to open a support case via the Meraki dashboard and ask to have it extended.
When using Meraki Authentication for Client VPN authentication, SSID association requirements, or MS Switch Access Policies, a network administrator can easily create and edit user accounts from the Meraki dashboard. Organization administrators can also delete existing user accounts. This article outlines how to create, edit or delete users for network access.
Creating Meraki Cloud Authentication Guest Users
In the dashboard, there are two types of Meraki Cloud Authentication accounts available: 'Guest' and 'Administrator'. Dashboard accounts (network and organization administrators) will be listed as administrators, while guests are user accounts that have been manually created.
Note: Meraki Authentication must be enabled on Client VPN or at least one SSID to be able to create, edit or delete users.
To create a guest account:
- From the dashboard, Navigate to Network-wide > Configure > Users. Select the SSID to configure from the SSID drop-down menu.
- Choose Add user.
- A pop-up window will appear to set the following attributes:
- Description: A descriptive name i.e. John Doe.
- Email (Username): The email address of the user account which is also the login name. Passwords will be sent to this address.
- Password: Enter a password or select the Generate button to generate a random password. The password can be emailed to the new user if desired.
- Authorize:Yes allows network access for the SSID selected, No denies network access.
- Expires: Choose the default of Never, or click Change and set the expiration value using the drop-down.
- Choose Createuser.
- Your new user will be now listed on your user list. Select Save changes at the bottom of the page, and wait a few minutes for the changes to take effect.
- The user will receive an email, notifying them about the account creation and allowing them to update their email or password.
Authorizing Administrators
Any dashboard administrator will be added to the Meraki Authentication users list automatically, but needs to be specifically authorized for the SSID or Client VPN:
- From the dashboard, navigate to Network-wide > Configure > Users. Select the SSID to configure from the SSID drop-down menu.
- Choose the administrator to be granted access.
- Change the Authorized field to Yes.
- Select Update user.
For more information about managing Dashboard administrator accounts, please refer to our documentation.
Permissions for Managing Meraki Cloud Authentication Guest Users
Note that the list of Meraki Cloud Authentication users is consistent across an organization. So, any 'Network' Administrator may administer any guest user in an organization provided that they have write access to at least one network. For a Network Administrator, this means they should be allowed to:
- Authorize or De-authorize the user for the network they have permission to
- Update the user (such as setting a new password, affecting the user account in all networks in the organization)
Editing Users
- From the dashboard, navigate to Network-wide > Configure > Users. Select the SSID to configure from the SSID drop-down menu.
- Choose on the user account you want to edit. A pop-up window will appear to edit the user's attributes. Make changes required and select Update user.
- Your edited user will be listed on your user list. Interact with Save changes at the bottom of the page, and wait a few minutes for the changes to take effect.
Note: A user can modify their own credentials and reset their password if they are not an administrator account by logging in through account.meraki.com/account/account_login. This page is only available for users created under SSID configured as splash or Client VPN.
Deleting Users
Note: Since the users list is consistent across an organization, only an Organization Administrator can delete users.
- In the dashboard, go to Network-wide > Configure > Users. Select the SSID from the SSID drop-down menu that contains the user account
- Select the X icon to the far right of the user account you wish to delete.
- Select the Save Settings button at the bottom of the page.
Meraki Client Vpn 2fa Windows 10
Deauthorizing Administrators
Since administrators on the users list are tied directly with existing Dashboard administrator accounts, they cannot be deleted from the users list. However, they can be allowed/prevented from using Client VPN or associating with a Meraki Authentication-enabled SSID by revoking their access:

- From the dashboard, navigate to Network-wide > Configure > Users. Select the SSID to configure from the SSID drop-down menu.
- Choose on the administrator to be revoked access.
- Change the Authorized field to No.
- Select Update user.
Meraki Vpn Client Setup
For more information about managing Dashboard administrator accounts, please refer to our documentation.
